Epoch 8 – Introduction to MVC in JSP/Servlets
Introduce the MVC architecture (Model–View–Controller) in the context of JSP/Servlet development. Compare it with Model 1 (direct JSP processing) used in earlier steps. Identify benefits and set the direction for adopting MVC in the E-Commerce web application.
Epoch 8 – Introduction to MVC in JSP/Servlets
1. What is MVC?
MVC (Model–View–Controller) is a software architectural pattern that separates the application into three main components:
| Component | Responsibility | Example in the project |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Represents the data and business logic. Contains POJO classes and DAO classes for database operations. | User.java, Product.java, UserDAO.java, ProductDAO.java |
| View | Handles the presentation layer. Displays data to users using HTML, CSS, JSTL, EL. No JDBC code here. | login.jsp, home.jsp, product_list.jsp |
| Controller | Acts as an intermediary: receives requests, calls the Model for processing, and selects the View for the response. | LoginServlet.java, LogoutServlet.java, ProductServlet.java |
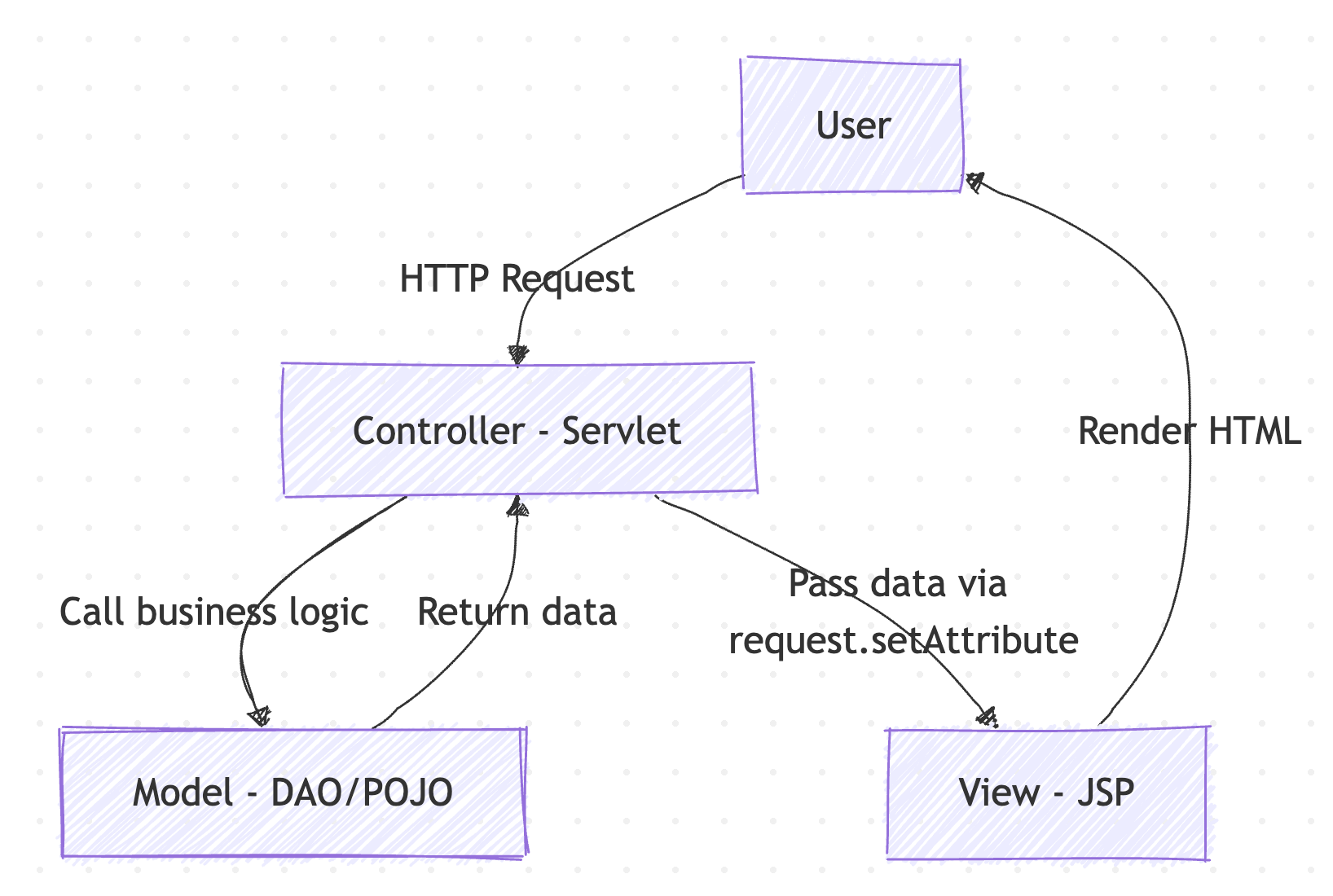
2. MVC Flow
- The user submits a request (e.g., a login form).
- The Controller (Servlet) receives the request and retrieves form data.
- The Controller calls the Model (DAO) to process business logic and query the database.
- The Model returns the result to the Controller.
- The Controller sets attributes using request.setAttribute(…) and forwards to a View (JSP).
- The View renders the result to the user.
Flow Diagram:
3. Model 1 vs Model 2 (MVC)
| Criteria | Model 1 (Direct JSP) | Model 2 (MVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Code organization | HTML, JDBC, and logic mixed in JSP | Separated into Model, View, Controller |
| Maintainability | Changing UI may break logic | UI and logic are separated, easier to maintain |
| Code reusability | Hard to reuse DAO/business logic | DAO and Model are reusable |
| Security | Logic code may be exposed to clients | Logic stays in Servlet, not exposed |
| Project scale | Fits small apps only | Scales well for medium/large projects |
4. Benefits of Applying MVC to the E-Commerce Project
- Clear role separation: Frontend developers focus on JSP/Bootstrap, backend developers focus on DAO and Servlets.
- Easy to extend: Features like shopping cart and order management can be added without breaking existing code.
- Reusable DAO classes: For example, UserDAO can be used for both login and admin user management.
- Professional learning: Helps students become familiar with industry patterns like Spring MVC, JSF, Struts, etc.
5. Direction for Epoch 9
Follow this folder structure:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/src/
├── Controllers
│ ├── LoginServlet.java
│ ├── LogoutServlet.java
├── Models
│ ├── User.java
├── DALs
│ ├── UserDAO.java
├── Utils
│ ├── DBContext.java
/webapp/
├── WEB-INF/
│ ├── web.xml
├── views/
│ ├── login.jsp
│ ├── logout.jsp
│ ├── home.jsp
- Move all JDBC code from JSP to DAO classes in /DALs.
- Create Servlet Controllers for each function (e.g., LoginServlet, LogoutServlet).
- Ensure JSP pages only contain HTML + JSTL, no JDBC scriptlets.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.