Getting Started
The Object Oriented Programming using Java (PRO192)
Getting Started
Object-Oriented Programming using Java
This subject introduces the student to object-oriented programming. The student learns to build reusable objects, encapsulate data and logic within a class, inherit one class from another and implement polymorphism. Adhere to object-oriented programming principles including encapsulation, polymorphism and inheritance when writing program code
Learning outcomes
- Understand the concepts of object oriented (OO) programs to solve problems and fundamentals of object-oriented programming in Java Practice basic Java language syntax and semantics to write Java programs and use concepts such as variables, conditional and iterative execution methods
- Uses streams to read and write data from/to different types of sources/targets
- Discuss the benefits and the use of JAVA’s Exceptional handling mechanism
- Identify classes, objects, members of a class and relationships among them needed for a specific problem
- Explain the concept and demonstrates the use of Polymorphism, Encapsulation, Abstraction and Inheritance in java Discuss the principles and the use of abstract classes and interfaces in java
- Understand and implement a complete program using object array Explain the principles and the use of some (java collections) abstract data types (list, set, map)
Academic policy
- Cheating, plagiarism and breach of copyright are serious offenses under this Policy.
- Cheating Cheating during a test or exam is construed as talking, peeking at another student’s paper or any other clandestine method of transmitting information.
- Plagiarism Plagiarism is using the work of others without citing it; that is, holding the work of others out as your own work. Breach of Copyright If you photocopy a textbook without the copyright holder’s permission, you violate copyright law.
Prerequisite(s)
PRF192 - Programming Fundamentals
Java Technology
Java technology is a high-level, robust, and secure programming platform. It includes:
- Java Programming Language: A powerful, object-oriented language.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): Executes Java bytecode and enables cross-platform functionality.
- Java Application Programming Interface (API): A large collection of ready-to-use libraries and tools.
The Java Programming Language
Java is:
- Object-Oriented: Based on objects and classes.
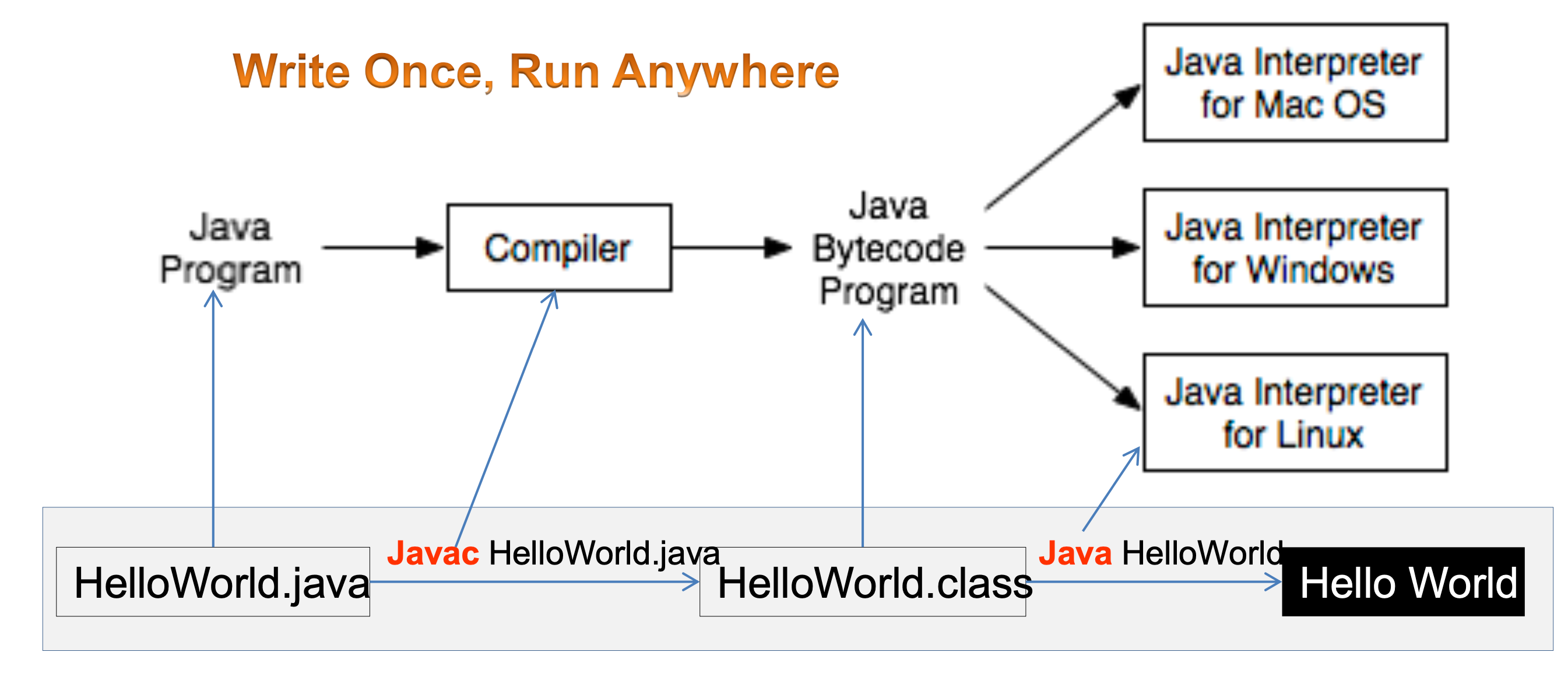
- Platform-Independent: Write once, run anywhere (WORA) through the JVM.
- Strongly Typed: Type checking at both compile-time and runtime.
- Syntax Similar to C/C++: Makes it easy for developers from those backgrounds.
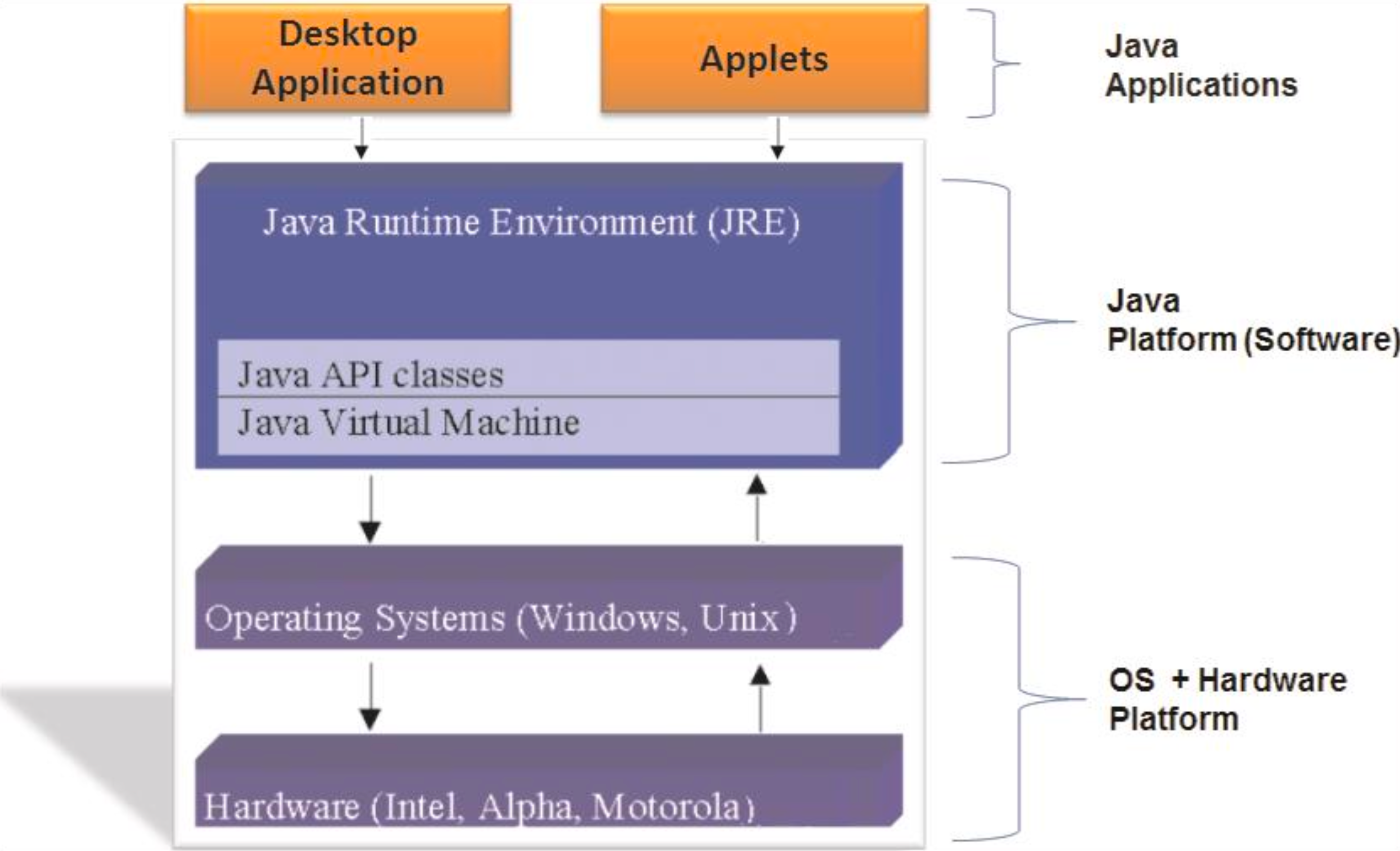
Java Platform
The Java platform includes:
- JDK (Java Development Kit): Tools for developing Java applications.
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment): Libraries and JVM needed to run Java applications.
- JVM (Java Virtual Machine): Core of the platform that runs bytecode.
Java Platform Editions
- Java SE (Standard Edition): Core functionality for general-purpose programming.
- Java EE (Enterprise Edition): Tools for enterprise-level applications (now Jakarta EE).
- Java ME (Micro Edition): Tailored for embedded systems and mobile devices.
- JavaFX: For developing rich GUI applications.
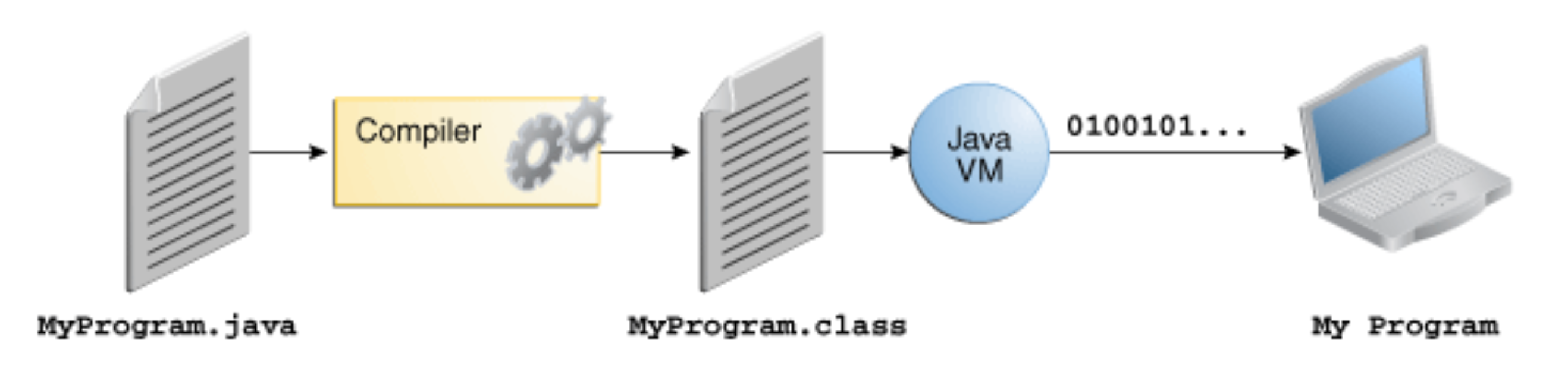
Bytecode
- What is Bytecode?: Intermediate, platform-independent code generated by the Java compiler.
- Executed by the JVM, not directly by the operating system.
- Enables portability, security, and performance optimization.
- Stored in
.classfiles after compiling.javasource files.
Example: A Simple Java Program
1
2
3
4
5
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.