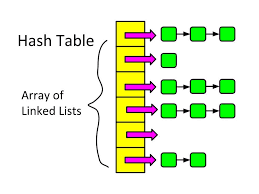
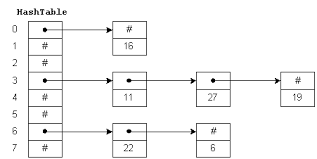
HashTable
Practice for Array-based Sequences such as HashTable
1. HashTable using Linked list
Hash tables are widely used to store and retrieve data efficiently. However, hash collisions are unavoidable.
In this assignment, you will implement a traditional hash table using separate chaining with linked lists to handle collisions.
You are not allowed to use Python built-in dictionaries (dict) or any hash table libraries.
Data Model
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | Key used for hashing |
| value | any | Value associated with the key |
| next | Node | Reference to the next node in the bucket |
Node Model
| Component | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| table | list | Array of linked lists (buckets) |
| size | int | Number of buckets |
| count | int | Number of stored key–value pairs |
Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
hash_function(key) | Compute hash index from key |
insert(key, value) | Insert or update a key–value pair |
search(key) | Retrieve value by key |
delete(key) | Remove key–value pair |
display() | Show full hash table structure |
load_factor() | Return current load factor |
1. hash_function(key)
Convert a key into an index of the hash table.
Work in:
- Convert each character in the key into its ASCII value.
- Sum all ASCII values.
- Apply modulo operation with table size.
Input
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | Key to be hashed |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| int | Index in range [0, table_size - 1] |
Ex:
1
hash_function("apple") => 3
2. insert(key, value)
Insert a new key–value pair into the hash table or update an existing key.
Work in:
- Compute the hash index using hash_function(key).
- Go to the linked list at that index.
- Traverse the list:
- If the key already exists => update its value.
- Otherwise => insert a new node at the end of the linked list.
- Increase element count if a new key is added.
Input
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | Key to insert |
| value | any | Value associated with the key |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| None | Prints insertion/update message |
Ex:
1
2
Key 'apple' inserted at index 3
Key 'apple' updated at index 3
search(key)
Retrieve the value associated with a given key.
Work in:
- Compute the hash index.
- Traverse the linked list at that index.
- Compare each node’s key with the search key.
- Return value if found.
Input
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | Key to search |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| any | Value associated with the key |
| None | If key is not found |
Ex:
1
2
Value for key 'banana': 20
Key 'orange' not found
delete(key)
Remove a key–value pair from the hash table.
Work in:
- Compute the hash index.
- Traverse the linked list at that index.
- Track both current and previous nodes.
- If the key is found:
- Update pointers to remove the node.
- Decrease element count.
Input
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| key | string | Key to remove |
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| bool | True if deletion successful, False otherwise |
Ex:
1
2
Key 'banana' removed from index 1
Key 'orange' not found
display()
Show the full internal structure of the hash table.
Work in:
- Iterate through each index of the table.
- Print the linked list stored at each bucket.
- Use arrows (->) to show chaining.
Output
Printed representation of the hash table.
Ex:
1
2
3
4
5
Hash Table:
[0] -> apple:10 -> mango:5
[1] -> banana:20
[2] -> empty
[3] -> grape:7
load_factor()
Measure how full the hash table is.
Work in:
- Divide number of stored elements by table size.
- load_factor = count / size
Output
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| float | Current load factor |
Ex:
1
Load factor: 0.6
2. Student Record Management System Using Hash Table
Universities need to store and retrieve student records efficiently. Searching student information using linear data structures becomes slow when the number of students increases.
In this assignment, you will design a Student Record Management System using a Hash Table implemented with linked lists to handle collisions.
This system will allow fast insert, search, and delete operations based on a student ID.
You are not allowed to use Python built-in dictionaries or hash table libraries.
Data Model
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| student_id | string | Unique student identifier |
| name | string | Student full name |
| major | string | Student major |
| next | Node | Pointer to next node in bucket |
StudentRecordManagement class
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
hash_function(student_id) | Compute bucket index |
add_student(id, name, major) | Insert or update student |
find_student(id) | Retrieve student record |
remove_student(id) | Delete student record |
display_all() | Show entire hash table |
load_factor() | Calculate load factor |
Input Specification
The program processes user commands from standard input.
Add or Update Student
1
ADD <student_id> <name> <major>
Ex:
1
ADD S123 Alice ComputerScience
Output:
1
Student S123 added at index 2
or
1
Student S123 updated at index 2
Find Student
1
FIND <student_id>
Output:
1
2
3
4
Student Found:
ID: S123
Name: Alice
Major: ComputerScience
or
1
Student S999 not found
Remove Student
1
REMOVE <student_id>
Output:
1
Student S123 removed from index 2
or
1
Student S999 not found
Display All Students
1
DISPLAY
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
Hash Table:
[0] -> S101 -> S202
[1] -> empty
[2] -> S123 -> S305
[3] -> S450
Exit Program
1
EXIT
3. Assignment: String-Based Hash Table for Dictionary Lookup
Many real-world applications rely on string keys, such as usernames, URLs, email addresses, and dictionary words.
In this assignment, you will implement a hash table that uses string-based hash functions to efficiently store and retrieve words and their definitions.
Collisions must be handled using separate chaining with linked lists.
You are not allowed to use Python built-in dictionaries or hashing utilities.
Data Model
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| word | string | Dictionary word (key) |
| meaning | string | Definition of the word |
| next | Node | Pointer to next node in bucket |
Hash Table Structure
| Component | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| table | List | Array of linked lists |
| size | int | Number of buckets |
| count | int | Number of stored words |
DictionaryLookup class
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
hash_function(word) | Compute hash index from string |
insert(word, meaning) | Add or update word |
search(word) | Find word definition |
delete(word) | Remove word |
display() | Show full hash table |
collision_count() | Return number of collisions |
Hash Function Specification (String-based)
Hash Formula:
1
2
3
hash = 0
for each character c in word:
hash = (hash * 31 + ASCII(c)) % table_size
- 31 is a commonly used prime number
- ASCII(c) is the ASCII value of character c
Input Specification
The program reads commands from standard input.
Add or Update Student
1
ADD ADD <word> <meaning>
Ex:
1
ADD algorithm "a step-by-step procedure"
Output:
1
Word 'algorithm' inserted at index 4
or
1
Word 'algorithm' updated at index 4
Search Word
1
FIND <word>
Output:
1
Meaning of 'algorithm': a step-by-step procedure
or
1
Word 'algorithm' not found
Delete Word
1
REMOVE <word>
Output:
1
Word 'algorithm' removed from index 4
or
1
Word 'algorithm' not found
Display All Students
1
DISPLAY
Output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Hash Table:
Hash Table:
[0] -> empty
[1] -> data["..."] -> structure["..."]
[2] -> empty
[3] -> queue["..."]
[4] -> algorithm["a step-by-step procedure"] -> array["a list"]
Exit Program
1
EXIT