Getting Started
This practice will be divided into three parts: - Part 01: Important tags in HTML5 - Part 02: Practical exercises with instructions - Part 03: Self-practice exercises -
1. Choose a tool for coding
You can use a number of tools to support website development such as Atom, Notepad++, Sublime Text, Adobe Dreamweaver CC, Visual Studio Code, CoffeeCup HTML Editor, Netbeans,…
Particularly for the LAB lessons in this course, I will use Visual Studio Code.
You can download Visual Studio Code via this link: https://code.visualstudio.com/download
After that, you proceed to install Visual Studio Code tools normally like other applications
2. Create a static web project
If you want to create a static web project, you can follow like this:
In the local computer, you can organize the folder structure on your computer as follows:
- Folder css: It contains .css files for styling your web page.
- Folder images: It contains image files which is used for your site. Moreover, you can create some folders such as video, audio,…and it is the same level with “images” folder.
- Folder js: It contains Javascript files (.js files) for interaction with your site.
- You can create many .html files in the same level with folders above. Or you can put .html files to other folders (depending on the intended use).
Academic policy
- Cheating, plagiarism and breach of copyright are serious offenses under this Policy.
- Cheating Cheating during a test or exam is construed as talking, peeking at another student’s paper or any other clandestine method of transmitting information.
- Plagiarism Plagiarism is using the work of others without citing it; that is, holding the work of others out as your own work. Breach of Copyright If you photocopy a textbook without the copyright holder’s permission, you violate copyright law.
Prerequisite(s)
PRF192 - Programming Fundamentals
Java Technology
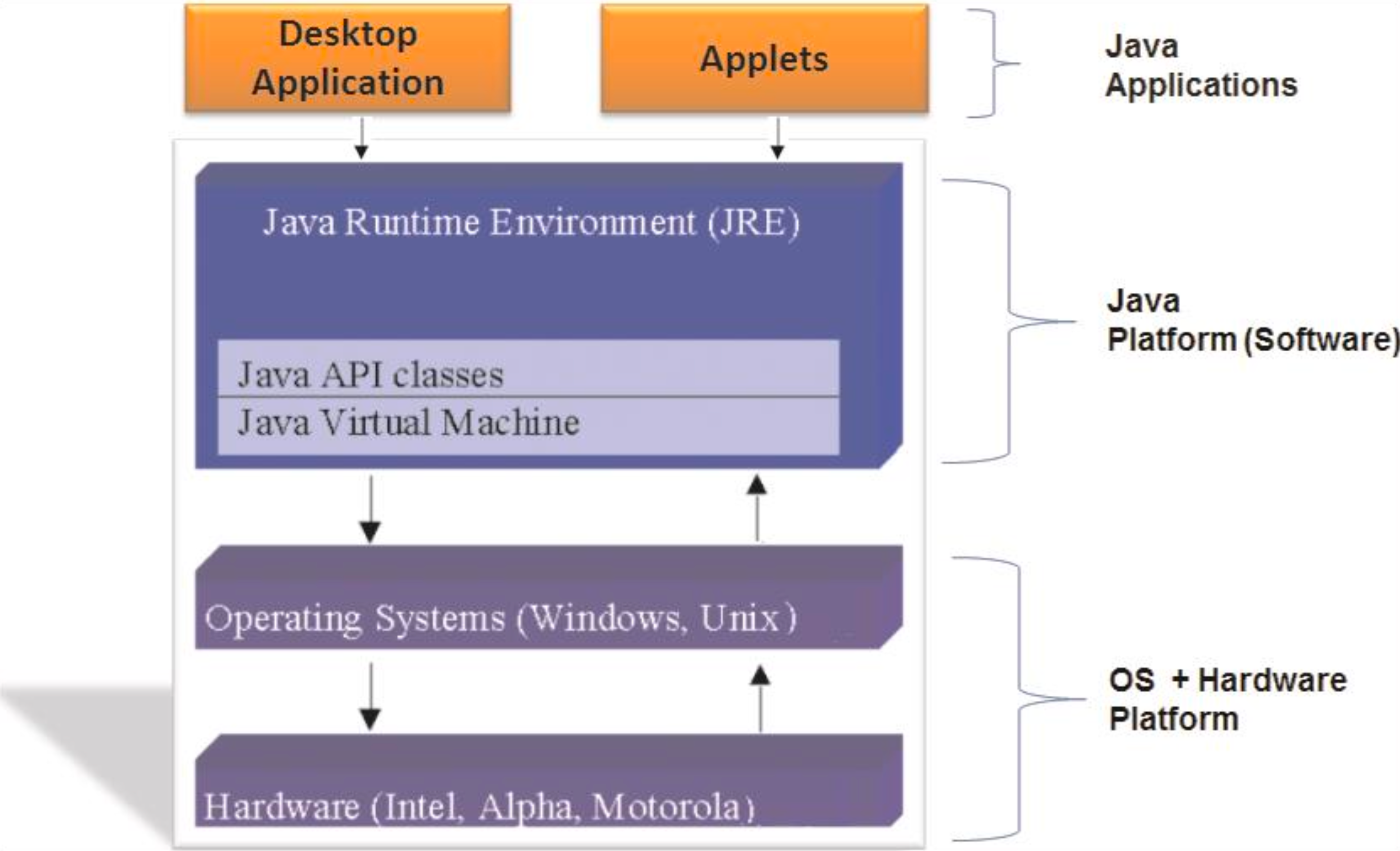
Java technology is a high-level, robust, and secure programming platform. It includes:
- Java Programming Language: A powerful, object-oriented language.
- Java Virtual Machine (JVM): Executes Java bytecode and enables cross-platform functionality.
- Java Application Programming Interface (API): A large collection of ready-to-use libraries and tools.
The Java Programming Language
Java is:
- Object-Oriented: Based on objects and classes.
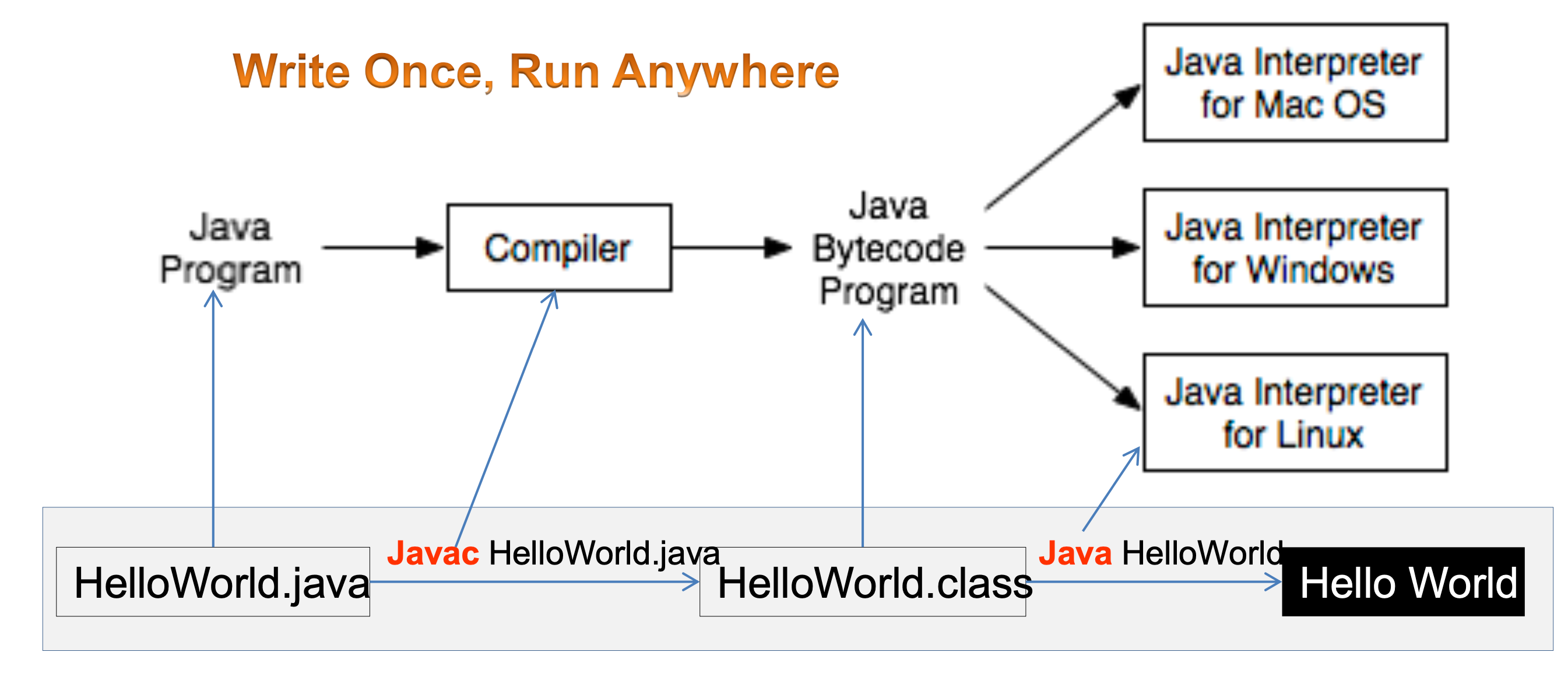
- Platform-Independent: Write once, run anywhere (WORA) through the JVM.
- Strongly Typed: Type checking at both compile-time and runtime.
- Syntax Similar to C/C++: Makes it easy for developers from those backgrounds.
Java Platform
The Java platform includes:
- JDK (Java Development Kit): Tools for developing Java applications.
- JRE (Java Runtime Environment): Libraries and JVM needed to run Java applications.
- JVM (Java Virtual Machine): Core of the platform that runs bytecode.
Java Platform Editions
- Java SE (Standard Edition): Core functionality for general-purpose programming.
- Java EE (Enterprise Edition): Tools for enterprise-level applications (now Jakarta EE).
- Java ME (Micro Edition): Tailored for embedded systems and mobile devices.
- JavaFX: For developing rich GUI applications.
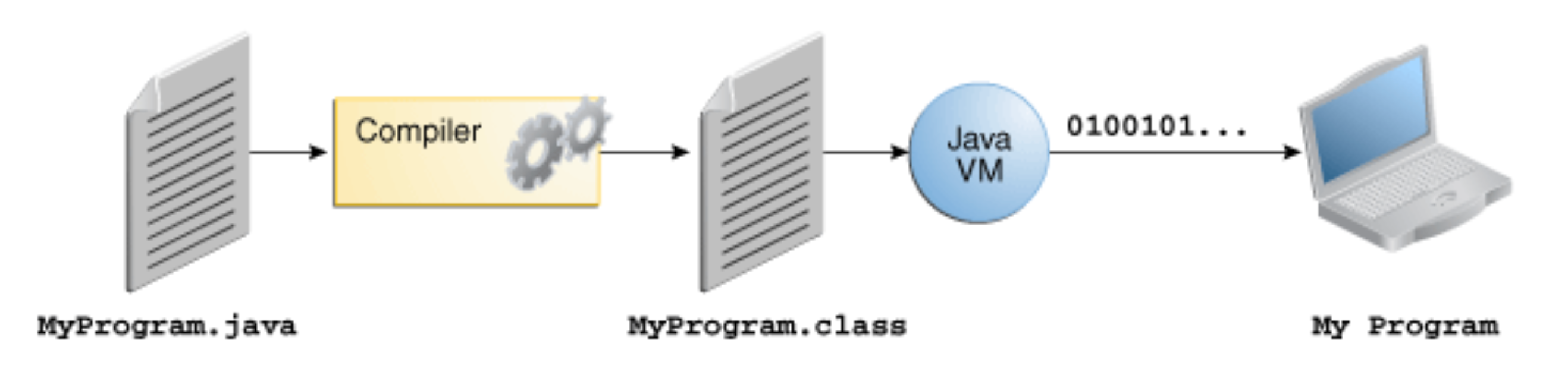
Bytecode
- What is Bytecode?: Intermediate, platform-independent code generated by the Java compiler.
- Executed by the JVM, not directly by the operating system.
- Enables portability, security, and performance optimization.
- Stored in
.classfiles after compiling.javasource files.
Example: A Simple Java Program
1
2
3
4
5
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}