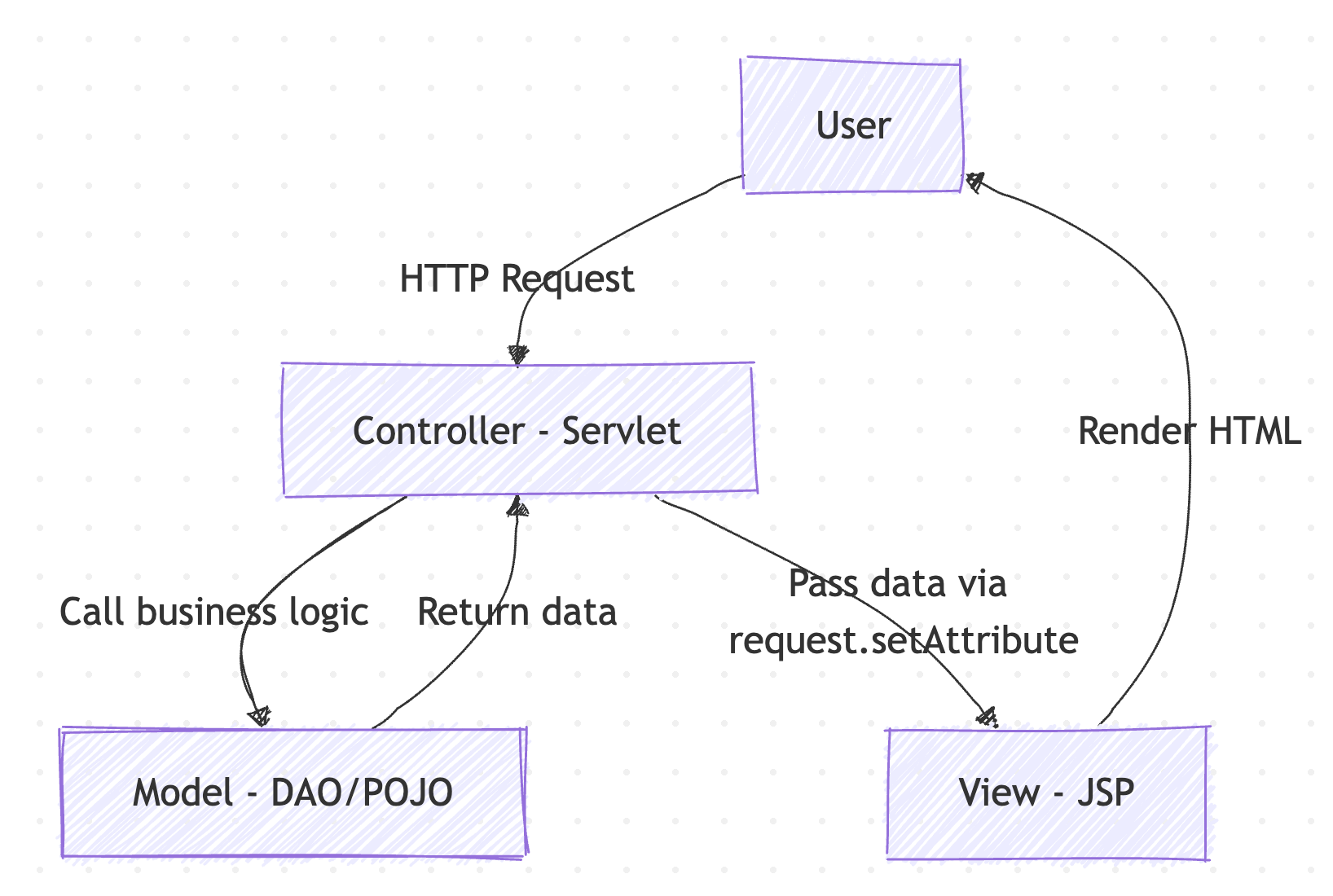
MVC (Model–View–Controller) is a software architectural pattern that separates the application into three main components:
| Component | Responsibility | Example in the project |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Represents the data and business logic. Contains POJO classes and DAO classes for database operations. | User.java, Product.java, UserDAO.java, ProductDAO.java |
| View | Handles the presentation layer. Displays data to users using HTML, CSS, JSTL, EL. No JDBC code here. | login.jsp, home.jsp, product_list.jsp |
| Controller | Acts as an intermediary: receives requests, calls the Model for processing, and selects the View for the response. | LoginServlet.java, LogoutServlet.java, ProductServlet.java |
Flow Diagram:

| Criteria | Model 1 (Direct JSP) | Model 2 (MVC) |
|---|---|---|
| Code organization | HTML, JDBC, and logic mixed in JSP | Separated into Model, View, Controller |
| Maintainability | Changing UI may break logic | UI and logic are separated, easier to maintain |
| Code reusability | Hard to reuse DAO/business logic | DAO and Model are reusable |
| Security | Logic code may be exposed to clients | Logic stays in Servlet, not exposed |
| Project scale | Fits small apps only | Scales well for medium/large projects |
Follow this folder structure:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/src/
├── Controllers
│ ├── LoginServlet.java
│ ├── LogoutServlet.java
├── Models
│ ├── User.java
├── DALs
│ ├── UserDAO.java
├── Utils
│ ├── DBContext.java
/webapp/
├── WEB-INF/
│ ├── web.xml
├── views/
│ ├── login.jsp
│ ├── logout.jsp
│ ├── home.jsp